AQG Yanadump↑
The AQG yanadump tool complements network analysis by enabling live traffic monitoring, providing continuous visibility into network activity.
It analyzes encrypted traffic within monitored connections, assessing the use of supported protocols and providing actionable insights without accessing exchanged data or relying on pre-captured PCAP files.
Requirements↑
- x64 architecture
- Linux kernel version:
>= 3.2for live capture>= 2.6.32for PCAP analysis
Download↑
You can download the AQG Network Analyzer from the web UI.
When to use Yanadump↑
Analyzing networks at the scale of gigabit Ethernet links presents challenges due to the high data volume. Since the data is too large to capture and save on disk, it needs to be analyzed as close to the network traffic as possible.
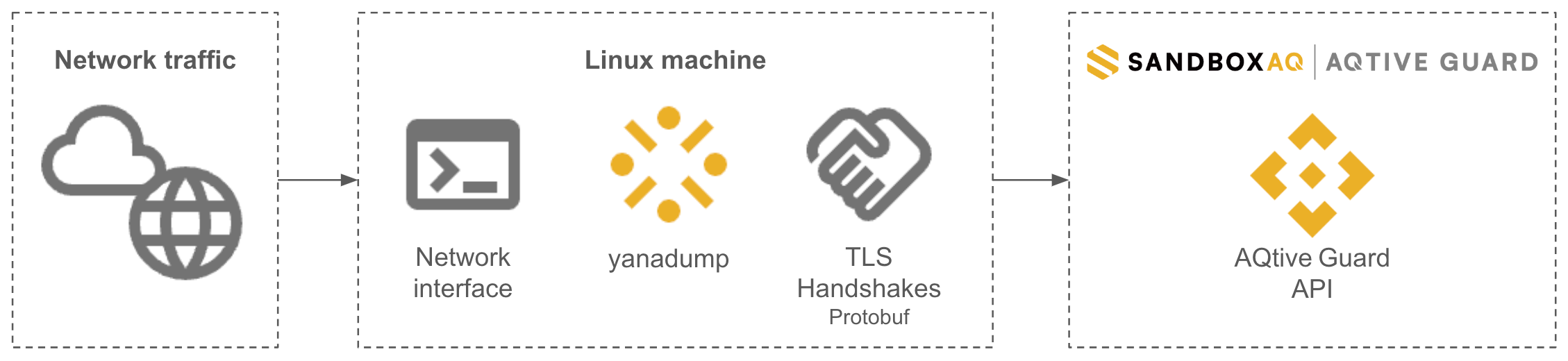
Yanadump is a high-efficiency network analyzer developed by SandboxAQ to capture and process cryptographic data on high-speed networks.
It operates as a standalone, portable Linux binary optimized for environments where high network speeds and large data volumes make storing full packet captures (PCAPs) impractical.
Instead of saving complete PCAP files, yanadump processes traffic in real time and generates compact Protobuf files containing only the relevant cryptographic details, as shown in the following diagram:
Key yanadump features include:
- Efficient Data Reduction: Reduces a 40GB PCAP to a 150MB Protobuf file (0.4% of original size), further compressible to 35MB (0.08%).
- Targeted Information: Extracts only handshake-related information, supporting efficient cryptographic analysis.
- Protocol Support: Supports Ethernet, 802.1Q (VLAN), GRE, IPv4, IPv6, and VXLAN, making it adaptable to various network configurations, including cloud environments.
- Scalability: Achieves traffic parsing speeds of approximately 1Gbps per CPU GHz, suitable for gigabit-scale networks.
- Resource Management: Controls maximum memory usage, preventing excessive resource utilization.